Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are two terms that people hear all the time in the world of technology. They are confused with each other and at times even used interchangeably. This leads to confusion. When it comes to machine learning, many people have been asking themselves what AI means when it is mentioned within its context. This process will be examined sequentially. / The following analysis will proceed in a systematic, stepwise manner.
Table of Contents
What is Artificial Intelligence.
In the simplest sense, Artificial Intelligence is the concept of having machines do work normally requiring human thought. These activities can be learning how to interpret human speech, recognizing images, solving a complex problem, or making decisions based on evaluating alternatives.
AI is not a single invention. It is rather a huge roof that a lot of techniques are put on. The larger vision of AI is to create machines that will behave in a way that we refer to as intelligent.

You may find instances of AI everywhere:
- Artificial intelligence like Siri or Alexa.
- Netflix and YouTube movie or video recommendations.
- Chatbots are there when you require assistance on websites.
- Self-driving cars.
All these are demonstrations of how machines are replicating a skill that we usually associate with the minds of humans.
The Place of Machine Learning
Machine learning constitutes a fundamental element of artificial intelligence.. It is one way to make AI happen. ML enables the computer to observe patterns and learn based on the data it gets, instead of writing thousands of rules that the computer should follow.
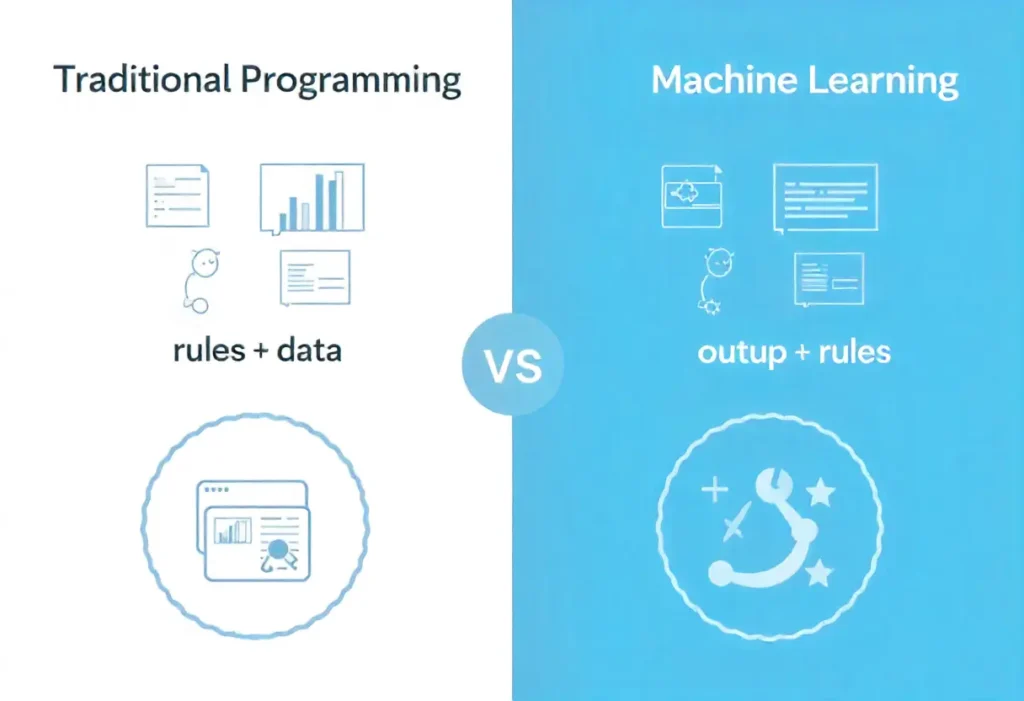
Here is another way to think about it:
In traditional programming, individuals input the rules and the data and the machine just returns the answer.
In machine learning, individuals input the data and the outcome and the machine determines the rules by itself.
The ability to learn through information is what makes machine learning really powerful. These systems instead of remaining fixed get better with time as additional information is processed. They can adapt themselves to new circumstances and solve those issues which we could not have solved at all without strict, rule-based instructions.
How AI and ML Work Hand in Hand
When a person refers to AI in machine learning, he or she typically refers to how machine learning techniques are utilised to produce intelligent behaviours. Machine learning serves as the foundational mechanism powering a majority of contemporary artificial intelligence systems.
It can be easily explained by a couple of examples:
ML models are used to assist machines in identifying objects within pictures or videos in computer vision.
“The objective of natural language processing, a domain within AI, is to equip computers with the capability to interpret and formulate human speech and text.”
“The implementation of machine learning enables dynamic difficulty adjustment, where computer-generated opponents evolve their tactics to align with the player’s skill level.”
In the absence of ML, AI would remain at an early stage, and would be confined to the rules that individuals type in manually.
Main Types of Learning in AI
Machine learning, which facilitates AI, typically comes in three forms:
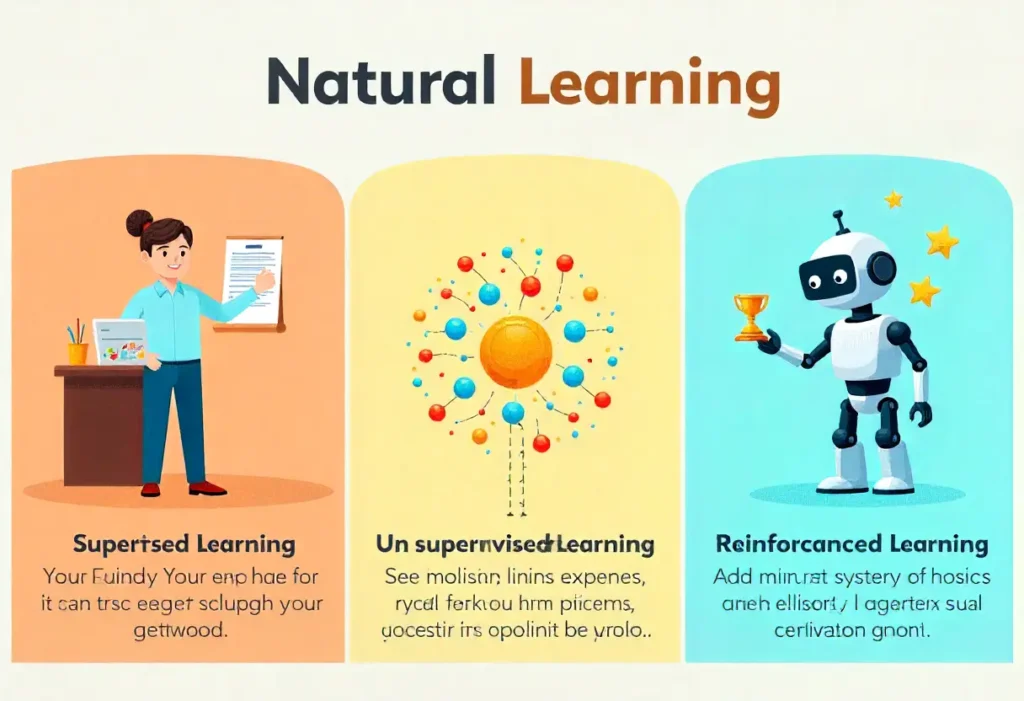
1. Supervised Learning
The system is trained using labeled data, i.e. the correct answers are known.
Example: Determining the value to which property may cost by comparing it to prior sales.
2. Unsupervised Learning
The system attempts to find patterns without knowing what the answer should be.
Example: An example is the division of customers into various groups based on the observation of trends that emerge in the purchase behavior of customers.
3. Reinforcement Learning
The system learns by trial and error and is rewarded by good behavior and punished by bad behavior.
Example: Programs that teach a robot to move itself or that teach software to play a game such as chess.
All forms serve some purpose, and AI relies on them in various circumstances.
AI and ML in the Real World
AI and ML are intertwined when you see real life. Here are some common areas:
Healthcare: AI systems with the help of ML scan and read medical images to support doctors and potentially identify diseases at an early stage.
Finance: Banks use ML models to identify abnormal transactions that can be indicative of fraud.
Online Shopping: E-commerce websites tend to suggest products based on your previous browsing and purchase history.
Transport: Autonomous vehicles have machine learning that identifies traffic lights, pedestrians, and other vehicles.
In all scenarios, the goal is AI, which is intelligent behavior, and the means of it is ML, or learning out of data.
Why the Difference Matters
The awareness of the connection between AI and ML prevents misconceptions. As an example, when individuals are afraid that AI is going to steal their jobs, they typically refer to machine learning systems that are used to automate specific tasks.
It also explains why data has become such a valuable asset in the current world. The performance of a machine learning model is contingent upon the quality and composition of its training dataset.
Data is great, but when one relies on it, it can get one into trouble. “The integrity of a model’s output is contingent upon the quality and fairness of its input data; flawed data inevitably produces flawed results.” That is why the ethical and responsible application of AI is gaining serious attention.
The Road Ahead
ML-driven AI is not finished yet. We have come a long way, but we still operate with the narrow AI that is good at certain tasks and bad beyond them.
And the aspiration of general AI, or a system capable of thinking, learning, and adapting to various disciplines in the same way humans do, has not been achieved. ML will probably continue to play a significant role in that journey, but the finish line is not very close yet.
Final thoughts
The answer to the question is simple: AI is the broader vision, machine learning is one of the tools that can get us there. Whereas AI relates to the creation of intelligent machines, ML allows such systems to develop and learn without the need to have pre-determined instructions.
The two are closely related. Collectively they are the foundations of technologies that are defining our daily lives: voice assistants, medical devices, fraud detection, and others. Their impact on society is bound to increase as they continue to grow.

Frequently Asked Questions For AI in Machine Learning
Q1: Well, then, what is the difference between AI and Machine Learning?
Actually, not quite. Artificial Intelligence is the large, general purpose of building smart machines. One of the primary ways that we get there is through Machine Learning. It is the section that is dedicated to learning through data.
Q2: What does Machine Learning actually attempt to do?
It is primarily aimed at developing systems that are able to examine information, identify patterns independently and then use what it identified to make predictions. The point is that it does all this without the individual being required to write out each step of the instruction step-by-step.
Q3: How does the learning part work at all?
It is learned through enormous amounts of information. The algorithm scans all of this data to identify common threads and constructs a model based on it. It then uses that model later to interpret new data that it has never encountered.
Q4: What is the simplest example that you can distinguish between them?
Sure. An example of a simple AI would be a thermostat that simply switches itself on when the temperature reaches a certain number. A **Machine Learning** system, however, is a recommendation system that calculates what you will like given everything you have ever watched or purchased previously .It adapts.

3 thoughts on “What is AI in Machine Learning?”